Government Policies & Incentives Boosting Electric Vehicles in India | 2025 Guide

India is accelerating towards a cleaner and greener mobility future with a robust push for electric vehicle (EV) adoption. Central and state governments are rolling out progressive EV policies, tax benefits, subsidies, and schemes to reduce the country’s carbon footprint and dependency on fossil fuels.
In this blog, we break down the key government policies and EV incentives in India (2025) that are shaping the country’s electric mobility ecosystem.
Why Government Policies Matter in EV Adoption
Electric vehicles come with higher upfront costs compared to conventional vehicles. However, government-backed incentives and support schemes help bridge the gap, making EVs accessible to both commercial and private users. These policies aim to:
- Reduce greenhouse gas emissions
- Lower import dependency on crude oil
- Boost domestic manufacturing
- Encourage EV infrastructure development
Key Central Government EV Policies & Incentives in India
1. FAME II Scheme (Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Hybrid & Electric Vehicles)
Launched: April 2019
Budget: ₹10,000 crore (extended till March 2024 and beyond into 2025)
Key Highlights:
- Offers upfront demand incentives on electric two-wheelers, three-wheelers, and buses.
- Promotes domestic EV manufacturing.
- Supports charging infrastructure setup.
EV Incentives under FAME II (2025):
- ₹15,000 per kWh for electric two-wheelers (subject to vehicle cap)
- Up to ₹50,000 for e-rickshaws and e-carts
- Large incentives for public electric buses and fleet operators
2. PLI Scheme for Advanced Chemistry Cell (ACC) Batteries
Objective: To reduce battery costs and enhance local manufacturing
Incentive: ₹18,100 crore
Focuses on:
- High-efficiency battery production
- Attracting foreign and local battery manufacturers
3. EV Tax Benefits (Income Tax Section 80EEB)
Benefit: Up to ₹1.5 lakh interest deduction on EV loan
Applicable for: Individual buyers who finance an EV purchase
4. GST Reduction on EVs
- GST on electric vehicles: Reduced to 5% (from 12%)
- GST on EV chargers: Reduced to 5%
State-Wise EV Policies in India (2025 Updates)
Delhi EV Policy
- Subsidy of up to ₹30,000 for e-two-wheelers
- ₹10,000 per kWh for e-four-wheelers (capped)
- Road tax and registration fees waived
Maharashtra EV Policy
- Incentives up to ₹1 lakh for electric cars
- Scrappage incentives up to ₹25,000
- Early bird incentives for first adopters
Gujarat EV Policy
- ₹10,000/kWh subsidy on EVs
- Focus on charging infrastructure in urban centers
Tamil Nadu EV Policy
- 100% exemption on road tax
- Incentives for OEMs and EV component manufacturers
Other States
Karnataka, Telangana, Rajasthan, and Uttar Pradesh are offering subsidies on vehicle purchase, manufacturing benefits, and charging infra support.
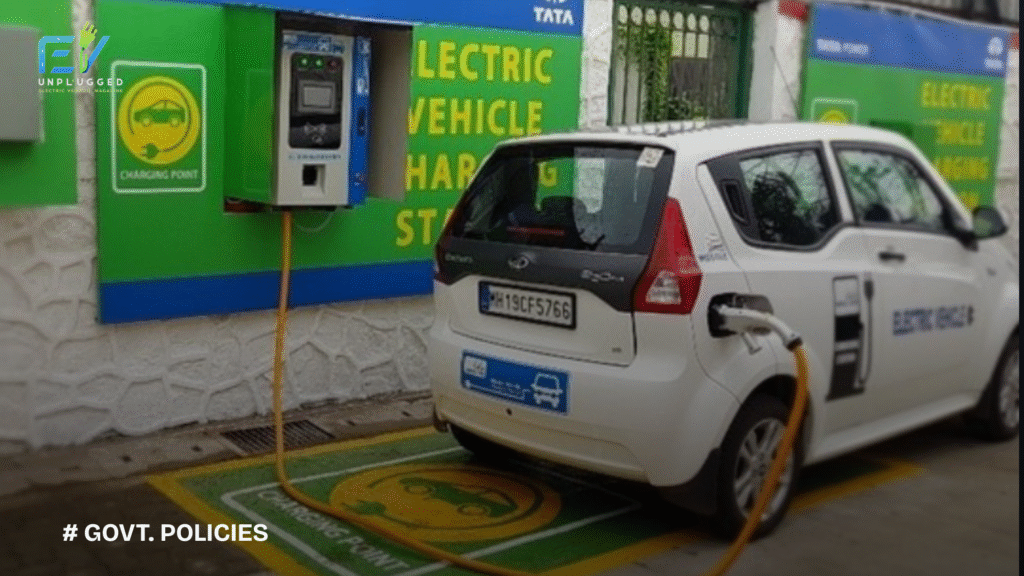
EV Infrastructure & Charging Station Support
The government is also investing in EV charging infrastructure through:
- Public-private partnerships (PPPs)
- Energy Efficiency Services Ltd. (EESL) programs
- Urban and highway charging corridors
- Battery swapping policies (being finalized)
Impact of Government EV Policies in 2025
These policies are already delivering results:
- EV registrations in India have surged by 50%+ year-on-year.
- EV startups and OEMs are expanding across Tier 2 and 3 cities.
- Job creation in the EV sector is on the rise.
Challenges Ahead
Despite strong policies, challenges remain:
- Inconsistent state-level implementation
- Charging infrastructure gaps in rural areas
- High battery costs and disposal concerns
Final Thoughts
India’s journey towards electric mobility is backed by a comprehensive mix of EV incentives, government schemes, and policy reforms. For individuals and businesses looking to invest in EVs in 2025, now is the right time to take advantage of these benefits.
Stay updated with evolving EV subsidy programs, tax exemptions, and state-specific policies to make the most of your electric mobility decision.


 English
English